Last Updated on April 19, 2024
Creating a wildlife hedge is a wonderful way to support biodiversity and contribute to the preservation of our natural environment. Wildlife hedges offer numerous benefits to both wildlife and humans, providing a haven for native species while also offering aesthetic appeal and privacy. In this article, we will explore why wildlife hedges are important and guide you through the process of creating and maintaining one.
What is a Wildlife Hedge?
A wildlife hedge is a strategically planted and managed barrier made up of diverse native plants that serve as a habitat for various wildlife species. Unlike conventional hedges, which are typically a single variety of plants, wildlife hedges consist of a wide range of plant species that offer shelter, food, and nesting opportunities for birds, insects, mammals, and other creatures.
 To create an effective wildlife hedge, it's important to consider the components that make it suitable for wildlife. These include a mixture of trees, shrubs, and perennials that provide year-round interest and resources. The structure of the hedge should be varied, with varying heights, thicknesses, and densities to accommodate different wildlife preferences.
To create an effective wildlife hedge, it's important to consider the components that make it suitable for wildlife. These include a mixture of trees, shrubs, and perennials that provide year-round interest and resources. The structure of the hedge should be varied, with varying heights, thicknesses, and densities to accommodate different wildlife preferences.
Planning and Site Selection
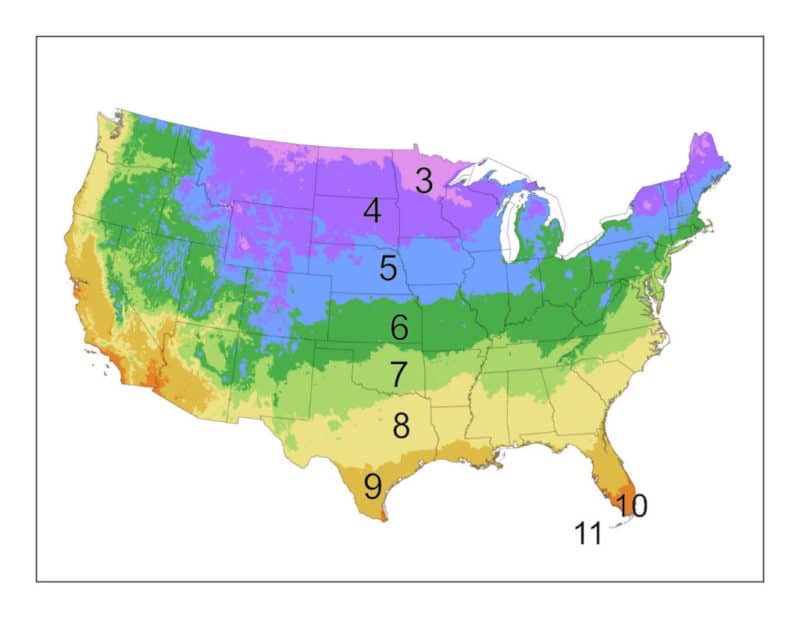
When considering creating a wildlife hedge, it's crucial to select the right location. Ideally, the hedge should be situated in an area that receives an appropriate amount of sunlight, avoiding areas with shade-heavy conditions. Soil quality and drainage should also be taken into account, as a well-drained site with fertile soil will promote healthy plant growth and an abundance of wildlife.
It is also important to consider external factors, such as neighboring land use, potential pollution sources, and existing wildlife corridors. These factors play a vital role in creating a sustainable and thriving habitat for wildlife.
 Selecting Suitable Plant Species
Selecting Suitable Plant Species
Choosing the right plant species for your wildlife hedge is essential for attracting and supporting a diverse range of wildlife. Native plants are highly recommended as they have coevolved with local wildlife and are well-suited to the environmental conditions of the area.
Different plants attract different types of wildlife, so it's beneficial to select a mix of plants that provide food, nesting opportunities, and shelter throughout the year. If you have room, usually 30 feet or longer, consider using more than one variety to create a dense wildlife hedge. Blackberry bushes usually have thorns, creating a natural defense for birds. Other berry-producing woody shrubs to consider include chokeberry, coralberry, viburnum, and serviceberry. Plant them in groups of 3 and make sure you include any required pollinator.
Mix in a few evergreens. Birds love berries from Junipers. Pyracantha is a thorny evergreen with berries that attract all sorts of wildlife. Most common holly shrubs are also ideal for nesting wildlife. The berries become an important food source, especially in winter when most other foods are scarce.
We have included a list of the most popular wildlife hedge plants below.
Planting and Establishment
Before planting your wildlife hedge, proper site preparation is essential. Clear any existing vegetation and ensure that the soil is adequately prepared by loosening it and incorporating organic matter to improve fertility and drainage. It is also important to consider the spacing between plants to allow them room to grow and to avoid overcrowding as the hedge matures.
Planting techniques vary depending on the plant species and conditions but generally involve digging a hole of appropriate size, placing the plant in, and backfilling with soil while firming gently around the roots. Adequate watering and mulching should be provided during the establishment period to promote healthy growth.
Maintenance and Care
Like any other garden feature, wildlife hedges require regular maintenance and care. Pruning and trimming are necessary to keep the hedge in shape, encourage a bushy growth habit, and remove any dead or diseased branches. However, it's crucial to avoid excessive pruning during the nesting season to prevent disturbing bird populations.
Weed control is also important to ensure the hedge has ample space and resources for its growth. Regular weeding and mulching can help suppress weed growth and conserve soil moisture. Additionally, protecting the hedge from pests, such as rabbits, may be necessary in regions where they pose a threat. Fencing or repellents can help safeguard the hedge until it reaches a height that deters these pests naturally.
Enhancing Biodiversity
One of the primary benefits of a wildlife hedge is its ability to support and enhance biodiversity. By providing suitable habitats and resources, wildlife hedges attract native species, acting as important corridors for wildlife movement and enabling gene flow between populations. The diverse plant species also attract and support pollinators, beneficial insects, and other vital components of a healthy ecosystem.
Long-term Benefits
Apart from their ecological value, wildlife hedges offer various long-term benefits. They contribute to erosion control and stabilize the soil, preventing runoff and improving water quality. Additionally, well-maintained wildlife hedges can greatly enhance the aesthetic appeal of a property, providing visual interest throughout the year. Moreover, they offer privacy and serve as a sound barrier, creating a tranquil environment.
 Incorporating Wildlife Features
Incorporating Wildlife Features
To further support wildlife, additional features can be incorporated within or near the wildlife hedge. Nest boxes and bird feeders provide additional nesting sites and food sources for birds, while water sources, such as birdbaths or small ponds, attract a wide range of wildlife, including amphibians and insects. Insect hotels provide shelter for solitary bees, ladybugs, and various other beneficial insects.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While creating a wildlife hedge is a rewarding endeavor, it may come with its challenges. Pests and diseases can pose a threat to the hedge's health and the wildlife it supports. Regular monitoring, early identification, and appropriate management strategies help combat these issues. Moreover, addressing maintenance difficulties, such as pruning or controlling invasive species, requires careful planning and perseverance.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of a Wildlife Hedge
Monitoring the wildlife populations and assessing habitat quality over time can help evaluate the effectiveness of a wildlife hedge. Regular observations of bird activity, insect populations, and changes in plant species diversity contribute to understanding the ecological success of the hedge. This information can guide further improvements and provide valuable insights for other conservation initiatives.
Conclusion
Creating a wildlife hedge is a powerful way to create habitat, support biodiversity, and contribute to the conservation of our natural environment. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can establish a thriving wildlife haven that not only provides a safe refuge for native species but also adds beauty and tranquility to your surroundings. Start today and make a positive impact on both wildlife and your local community.
Wildlife Hedge Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take for a wildlife hedge to establish?
The time it takes for a wildlife hedge to establish varies depending on several factors, including plant species, climate, and overall site conditions. Generally, it can take between 2 to 5 years for a wildlife hedge to reach maturity and provide optimal habitat for wildlife.
Can I create a wildlife hedge in a small garden?
Absolutely! Even in small gardens, it is possible to create a wildlife hedge that can support a diverse range of species. Compact and dwarf plant varieties can be chosen to fit the available space without compromising the habitat's functionality.
Are there any legal restrictions on planting wildlife hedges?
Legal restrictions regarding wildlife hedges may vary between regions and countries. It's always important to check local regulations, especially when dealing with protected species or specific land designations. Consulting with local authorities or conservation organizations can provide guidance in this regard.
Can I incorporate fruit-bearing plants in my wildlife hedge?
Yes! Incorporating fruit-bearing plants in your wildlife hedge can provide an additional food source for birds and mammals. Species like hawthorn, blackberry, and wild cherry are excellent choices to attract wildlife while also enjoying the fruits yourself.
Do wildlife hedges require a lot of water?
Established wildlife hedges typically require minimal watering, as native plants are adapted to local conditions. However, during the establishment phase, regular watering is necessary to help the plants establish strong root systems. Once established, wildlife hedges are generally resilient and can tolerate periods of drought.
8 Most Popular Wildlife Hedges
Common Name |
Botnical Name |
Popular Varieties |
| Barberry | Berberis thunbergii | Admiration, Orange Rocket, Sunjoy Gold Pillar |
| Holly | ilex | Nellie Stevens, Steeds, Oakland |
| Hazel | Corylus | Common, American Hazelnut |
| Juniper | Juniperus | Blue Point, Hollywood, Wichita Blue |
| Hawthorn | Rhaphiolepis | Indian, Pink Lady |
| Blackthorn | Prunus spinosa | Fine Line, Proven Winners |
| Viburnum | Viburnum | Spring Bouquet, Snowball, Popcorn |
| Ligustrum | Ligustrum japonicum | Wax leaf, Sunshine, Curly Leaf |
- Summer’s Saviors: 7 Drought Tolerant Perennials to Plant Now - July 26, 2024
- Why Your New Plants Sleep, Creep, Leap - July 26, 2024
- 5 Easy Landscape Tips to Increase Your Home Value - June 28, 2024

 Selecting Suitable Plant Species
Selecting Suitable Plant Species Incorporating Wildlife Features
Incorporating Wildlife Features